Written by Johann Nunez
Technical Sales Representative
February 19th, 2025
The air we breathe is composed of a complex mixture of gases, most of which are harmless. However, the presence of toxic or flammable gases in industrial settings can pose severe risks to both personnel and infrastructure. Exposure to hazardous gases—whether through leaks, process emissions, or accidental releases—can lead to health complications, explosions, and operational disruptions.
Gas detection is a critical component of workplace safety, allowing for the early identification of dangerous conditions before they escalate into life-threatening emergencies. Toxic gases can cause anything from mild irritation to fatal poisoning, while combustible gases create explosion risks that can result in devastating consequences. Without a reliable monitoring system, these hazards may remain undetected, putting both people and assets at risk.
Advancements in gas detection technology have significantly improved workplace safety. From basic detection methods to sophisticated real-time monitoring systems, industries now have access to a wide range of technologies designed to detect, measure, and mitigate gas-related risks. This article explores the most widely used gas detection technologies, their applications, and how they enhance safety in industrial environments.
What you’ll learn:
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of:
The risks posed by toxic and combustible gases and their impact on workplace safety.
The role of fixed gas detection systems in monitoring and preventing hazardous conditions.
The advantages and limitations of various gas detection technologies, including electrochemical, infrared, catalytic bead, and paper tape sensors.
The differences between open path gas detection and tunable diode laser (TDL) technology for large-area monitoring.
Choosing the right gas detection solution based on operational needs and environmental conditions.
The Risks of Toxic and Combustible Gases.
In many industrial environments, gases are integral to production, refining, or manufacturing processes. However, when these gases escape their intended containment, they can quickly become hazardous.
Toxic gases such as carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen sulphide (H₂S), and ammonia (NH₃) are particularly dangerous because they can be harmful even at low concentrations. These gases interfere with normal physiological functions, leading to symptoms that range from dizziness and nausea to respiratory failure and death. Some, like hydrogen sulphide, are highly toxic and can cause immediate collapse upon inhalation in high concentrations.
Combustible gases, including methane (CH₄), propane (C₃H₈), and hydrogen (H₂), pose a different type of risk. When these gases accumulate in confined spaces and mix with air at specific ratios, they become highly flammable. A single spark or heat source can ignite them, leading to explosions that can cause severe structural damage and loss of life.
Given these risks, continuous monitoring is essential to ensure that gas concentrations remain within safe limits. Fixed gas detection systems provide an effective solution, offering real-time data and early warning alerts that allow operators to take immediate action.
Fixed Gas Detection Systems: A Comprehensive Approach to Safety.
A well-designed gas detection system is more than just an alarm—it’s a fully integrated safety mechanism that monitors and mitigates risks in real-time. Fixed gas detection systems are widely used in industrial settings where gas leaks can occur, including oil refineries, chemical plants, and confined spaces like tunnels or underground storage facilities.
These systems consist of strategically placed sensors that continuously measure gas concentrations in the air. When dangerous levels are detected, the system triggers alarms, activates ventilation systems, or initiates shutdown procedures to prevent escalation. Advanced models can also integrate with control systems, allowing remote monitoring and automated responses.
Recent advancements in gas detection technology have enhanced both accuracy and efficiency. Miniaturization of sensors has allowed for more compact and energy-efficient designs, while improvements in detection techniques have increased the reliability of measurements. With better selectivity and reduced maintenance requirements, modern gas detection systems provide unparalleled protection for both personnel and infrastructure.
To maximize safety, choosing the right detection technology is crucial based on the specific gases present and the facility’s environmental conditions.
Gas Detection Technologies: How They Work and When to Use Them.
Paper Tape Sensors: A Basic but Effective Method
One of the simplest gas detection methods is the paper tape sensor, which relies on chemically treated paper to indicate the presence of certain gases. When exposed to a target gas, the paper undergoes a chemical reaction, resulting in a visible colour change. While this cost-effective method does not require a power source, it is primarily used in applications where real-time monitoring is not critical.
Paper tape sensors are best suited for remote locations or as backup detection tools. However, more advanced sensor technologies are preferred for environments requiring continuous and highly accurate gas monitoring.


Electrochemical Sensors: Precision in Detecting Toxic Gases
Electrochemical sensors are widely used for detecting toxic gases in industrial environments. These sensors operate by facilitating a chemical reaction between the target gas and an electrolyte solution. This reaction generates an electrical current proportional to the gas concentration.
The key advantages of electrochemical sensors include high sensitivity and selectivity, making them particularly useful for detecting low concentrations of hazardous gases. They are commonly deployed in confined spaces, manufacturing plants, and environments where toxic gas exposure is a major concern. However, regular calibration and sensor replacement are required to maintain accuracy over time.
Reliable gas detection starts with the right technology!
The Meridian Gas Detector combines advanced electrochemical sensors with smart features for superior workplace safety.
Combustible Gas Detection: Catalytic Bead vs. Infrared Sensors
Combustible gas detection is essential in industries where flammable gases are handled or stored. Two primary sensor technologies are used for this purpose: catalytic bead and infrared (IR) sensors.
Catalytic bead sensors work by oxidizing combustible gases on a heated wire coated with a catalyst. This reaction generates heat, which is measured to determine gas concentration. While catalytic bead sensors are cost-effective and widely used, they require regular maintenance due to catalyst degradation.
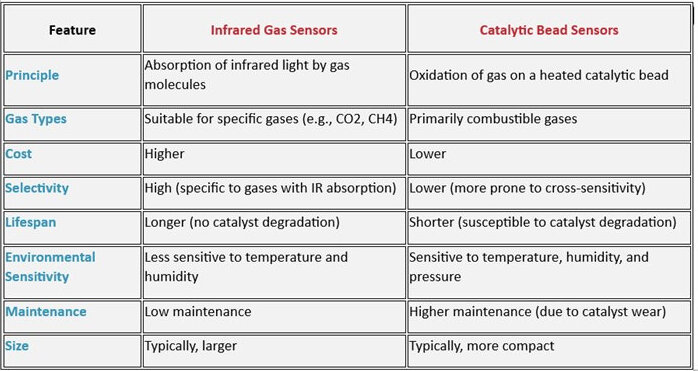
Infrared gas sensors, on the other hand, detect gases by analyzing how they absorb infrared light at specific wavelengths. Since each gas has a unique absorption pattern, IR sensors provide precise measurements with minimal cross-sensitivity. They also have a longer lifespan and lower maintenance requirements compared to catalytic bead sensors, making them ideal for applications where long-term reliability is critical.
Minimize maintenance and maximize safety.
The GD10P delivers stable, long-term gas detection—no calibration needed.
Advanced Monitoring: Open Path and Tunable Diode Laser (TDL) Detection.
For large-scale industrial facilities, point detection may not always be sufficient. Open path gas detection and tunable diode laser (TDL) technology provide broader coverage and enhanced monitoring capabilities.
Open-path gas detection uses an infrared beam to monitor gas concentrations across a large area. When a gas cloud crosses the beam, the sensor detects changes in light absorption, allowing for immediate identification of gas leaks. This method is particularly effective in outdoor environments or large production facilities where conventional point detectors might be insufficient.
Tunable diode laser (TDL) technology offers an even higher level of precision. By emitting a laser at a specific wavelength, TDL sensors can detect trace amounts of gases with minimal interference from other environmental factors. This technology is commonly used in chemical processing plants and refineries, where even minute gas leaks can pose serious risks.
For large-scale gas monitoring, precision matters.
The LaserGas™ II OP delivers real-time detection up to 1000m with advanced TDL technology. Ensure accurate, long-range monitoring with minimal maintenance.
Choosing the Right Gas Detection Solution.
Selecting the appropriate gas detection system depends on several factors, including the type of gas present, the operational environment, and safety regulations. Electrochemical sensors are ideal for detecting toxic gases, while catalytic bead and infrared sensors provide reliable combustible gas detection. Open path and TDL technologies offer superior coverage and precision for large-area monitoring.
Regardless of the technology chosen, regular maintenance and calibration are essential to ensure long-term reliability. A well-implemented gas detection strategy protects workers and assets and ensures compliance with industry safety standards.
As technology continues to advance, gas detection will become even more sophisticated, integrating with automation systems and AI-driven analytics to enhance predictive safety measures. Investing in the proper detection technology today is an essential step toward a safer, more efficient workplace.
Be the first to read our articles

Written by Johann Nunez
Technical Sales Representative
Write to Johann at: NunezJ@novatech.ca

